Introduction
In this section we will introduce the concept of graph neural networks and the notion of homophily. These concepts are important for understanding our machine learning model and the techniques we used to develop it.
Graph Neural Networks
Graph neural networks (GNNs) are a type of neural network that operates directly on graph data. Unlike traditional neural networks, which operate on fixed-size vectors, GNNs can handle variable-sized inputs and outputs. This makes them well-suited for tasks such as node classification, link prediction, and graph classification.
GNNs work by propagating information across the edges of a graph. Each node in the graph is represented by a feature vector, and the GNN updates these feature vectors by aggregating information from neighboring nodes. This process is repeated for multiple layers, allowing the GNN to capture complex patterns in the graph data.
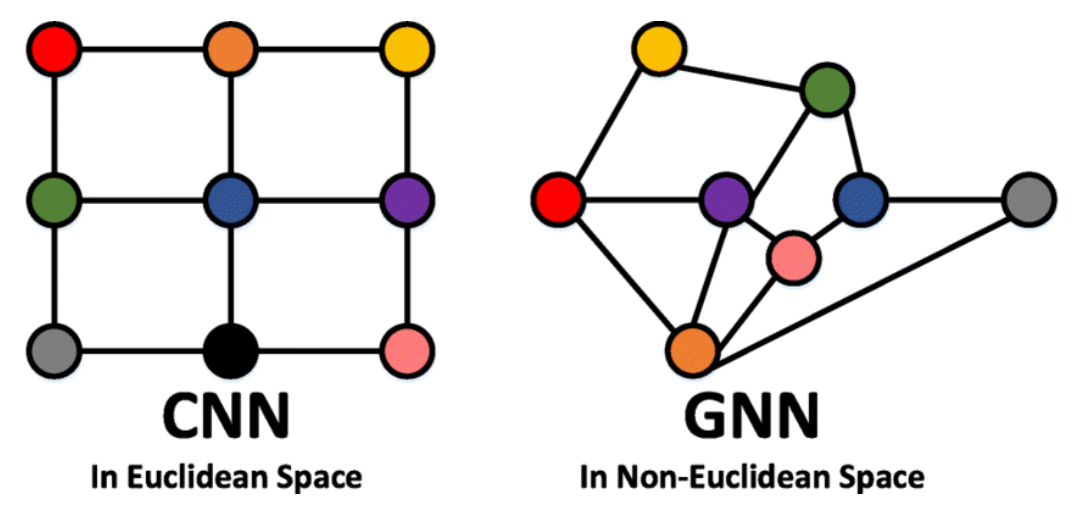
GNN can be seen as an extension of CNN to any topology.
Homophily
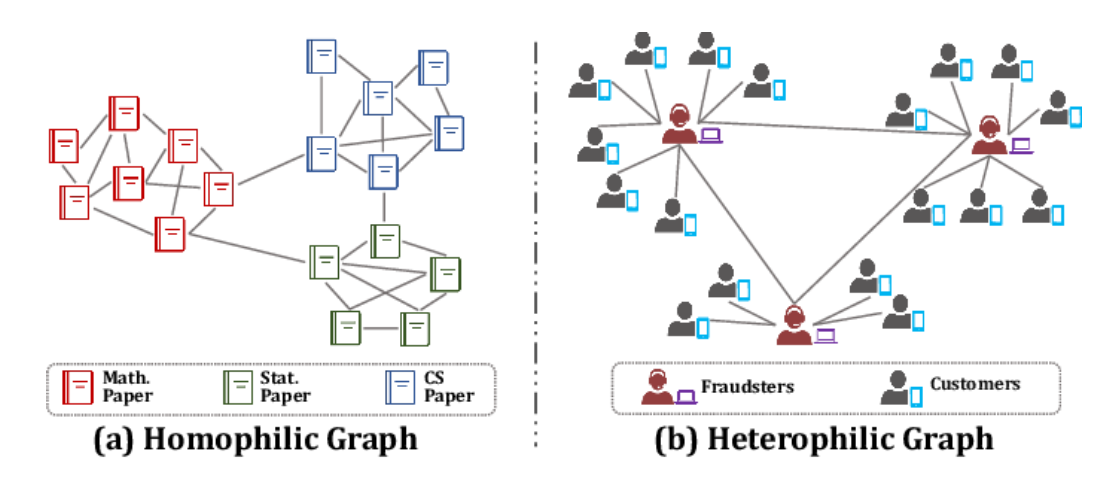
Homophily is the tendency for nodes in a graph to be connected to other nodes that are similar to them. This concept is important in the context of graph neural networks, as it can affect the performance of the model.
In a graph with high homophily, nodes that are connected to each other tend to have similar feature vectors. This makes it easier for the GNN to learn patterns in the data and make accurate predictions. However, in a graph with low homophily, connected nodes may have very different feature vectors, which can make it more difficult for the GNN to learn useful representations.
Understanding the level of homophily in a graph is an important step in developing a graph neural network. By taking homophily into account, we can design a model that is tailored to the specific characteristics of the graph data.
In the next section, we will go over the details of our machine learning model and how we used graph neural networks and homophily to make accurate predictions.